CTYPEia keyword for validity and returns information derived from it.
 -type spectral variables for the
-type spectral variables for the  -type variables supplied.
-type variables supplied.
 -type variables for the
-type variables for the  -types supplied.
-types supplied.
CTYPEia. #include "spx.h"Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | spcprm |
| Spectral transformation parameters. More... | |
Defines | |
| #define | SPCLEN (sizeof(struct spcprm)/sizeof(int)) |
| Size of the spcprm struct in int units. | |
| #define | spcini_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | spcprt_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | spcset_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | spcx2s_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
| #define | spcs2x_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| Deprecated. | |
Functions | |
| int | spcini (struct spcprm *spc) |
| Default constructor for the spcprm struct. | |
| int | spcprt (const struct spcprm *spc) |
| Print routine for the spcprm struct. | |
| int | spcset (struct spcprm *spc) |
| Setup routine for the spcprm struct. | |
| int | spcx2s (struct spcprm *spc, int nx, int sx, int sspec, const double x[], double spec[], int stat[]) |
| Transform to spectral coordinates. | |
| int | spcs2x (struct spcprm *spc, int nspec, int sspec, int sx, const double spec[], double x[], int stat[]) |
| Transform spectral coordinates. | |
| int | spctyp (const char ctype[], char stype[], char scode[], char sname[], char units[], char *ptype, char *xtype, int *restreq) |
Spectral CTYPEia keyword analysis. | |
| int | spcspx (const char ctypeS[], double crvalS, double restfrq, double restwav, char *ptype, char *xtype, int *restreq, double *crvalX, double *dXdS) |
| Spectral keyword analysis. | |
| int | spcxps (const char ctypeS[], double crvalX, double restfrq, double restwav, char *ptype, char *xtype, int *restreq, double *crvalS, double *dSdX) |
| Spectral keyword synthesis. | |
| int | spctrn (const char ctypeS1[], double crvalS1, double cdeltS1, double restfrq, double restwav, char ctypeS2[], double *crvalS2, double *cdeltS2) |
| Spectral keyword translation. | |
Variables | |
| const char * | spc_errmsg [] |
| Status return messages. | |
Routine spcini() is provided to initialize the spcprm struct with default values, and another, spcprt(), to print its contents.
A setup routine, spcset(), computes intermediate values in the spcprm struct from parameters in it that were supplied by the user. The struct always needs to be set up by spcset() but it need not be called explicitly - refer to the explanation of spcprm::flag.
spcx2s() and spcs2x() implement the WCS spectral coordinate transformations. In fact, they are high level driver routines for the lower level spectral coordinate transformation routines described in spx.h.
A number of routines are provided to aid in analysing or synthesising sets of FITS spectral axis keywords:
CTYPEia keyword for validity and returns information derived from it.
 -type spectral variables for the
-type spectral variables for the  -type variables supplied.
-type variables supplied.
 -type variables for the
-type variables for the  -types supplied.
-types supplied.
CTYPEia.
Spectral variable types -  ,
, 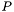 , and
, and  :
:
A few words of explanation are necessary regarding spectral variable types in FITS.
Every FITS spectral axis has three associated spectral variables:
 -type: the spectral variable in which coordinates are to be expressed. Each
-type: the spectral variable in which coordinates are to be expressed. Each  -type is encoded as four characters and is linearly related to one of four basic types as follows:
-type is encoded as four characters and is linearly related to one of four basic types as follows:
F: frequency 'FREQ': frequency 'AFRQ': angular frequency 'ENER': photon energy 'WAVN': wave number 'VRAD': radio velocity
W: wavelength in vacuo 'WAVE': wavelength 'VOPT': optical velocity 'ZOPT': redshift
A: wavelength in air 'AWAV': wavelength in air
V: velocity 'VELO': relativistic velocity 'BETA': relativistic beta factor
The  -type forms the first four characters of the
-type forms the first four characters of the CTYPEia keyvalue, and CRVALia and CDELTia are expressed as  -type quantities so that they provide a first-order approximation to the
-type quantities so that they provide a first-order approximation to the  -type variable at the reference point.
-type variable at the reference point.
Note that 'AFRQ', angular frequency, is additional to the variables defined in WCS Paper III.
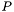 -type: the basic spectral variable (F, W, A, or V) with which the
-type: the basic spectral variable (F, W, A, or V) with which the  -type variable is associated (see list above).
-type variable is associated (see list above).
For non-grism axes, the 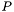 -type is encoded as the eighth character of
-type is encoded as the eighth character of CTYPEia.
 -type: the basic spectral variable (F, W, A, or V) for which the spectral axis is linear, grisms excluded (see below).
-type: the basic spectral variable (F, W, A, or V) for which the spectral axis is linear, grisms excluded (see below).
For non-grism axes, the  -type is encoded as the sixth character of
-type is encoded as the sixth character of CTYPEia.
Grisms: Grism axes have normal  -, and
-, and 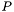 -types but the axis is linear, not in any spectral variable, but in a special "grism parameter". The
-types but the axis is linear, not in any spectral variable, but in a special "grism parameter". The  -type spectral variable is either W or A for grisms in vacuo or air respectively, but is encoded as 'w' or 'a' to indicate that an additional transformation is required to convert to or from the grism parameter. The spectral algorithm code for grisms also has a special encoding in
-type spectral variable is either W or A for grisms in vacuo or air respectively, but is encoded as 'w' or 'a' to indicate that an additional transformation is required to convert to or from the grism parameter. The spectral algorithm code for grisms also has a special encoding in CTYPEia, either 'GRI' (in vacuo) or 'GRA' (in air).
In the algorithm chain, the non-linear transformation occurs between the  -type and the
-type and the 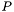 -type variables; the transformation between
-type variables; the transformation between 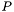 -type and
-type and  -type variables is always linear.
-type variables is always linear.
When the 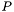 -type and
-type and  -type variables are the same, the spectral axis is linear in the
-type variables are the same, the spectral axis is linear in the  -type variable and the second four characters of
-type variable and the second four characters of CTYPEia are blank. This can never happen for grism axes.
As an example, correlating radio spectrometers always produce spectra that are regularly gridded in frequency; a redshift scale on such a spectrum is non-linear. The required value of CTYPEia would be 'ZOPT-F2W', where the desired  -type is '
-type is 'ZOPT' (redshift), the 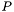 -type is necessarily 'W' (wavelength), and the
-type is necessarily 'W' (wavelength), and the  -type is 'F' (frequency) by the nature of the instrument.
-type is 'F' (frequency) by the nature of the instrument.
Argument checking:
The input spectral values are only checked for values that would result in floating point exceptions. In particular, negative frequencies and wavelengths are allowed, as are velocities greater than the speed of light. The same is true for the spectral parameters - rest frequency and wavelength.
Accuracy:
No warranty is given for the accuracy of these routines (refer to the copyright notice); intending users must satisfy for themselves their adequacy for the intended purpose. However, closure effectively to within double precision rounding error was demonstrated by test routine tspc.c which accompanies this software.
| #define SPCLEN (sizeof(struct spcprm)/sizeof(int)) |
Size of the spcprm struct in int units, used by the Fortran wrappers.
| #define spcini_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| #define spcprt_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| #define spcset_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| #define spcx2s_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| #define spcs2x_errmsg spc_errmsg |
| int spcini | ( | struct spcprm * | spc | ) |
spcini() sets all members of a spcprm struct to default values. It should be used to initialize every spcprm struct.
| [in,out] | spc | Spectral transformation parameters. |
| int spcprt | ( | const struct spcprm * | spc | ) |
spcprt() prints the contents of a spcprm struct.
| [in] | spc | Spectral transformation parameters. |
| int spcset | ( | struct spcprm * | spc | ) |
spcset() sets up a spcprm struct according to information supplied within it.
Note that this routine need not be called directly; it will be invoked by spcx2s() and spcs2x() if spcprm::flag is anything other than a predefined magic value.
| [in,out] | spc | Spectral transformation parameters. |
| int spcx2s | ( | struct spcprm * | spc, | |
| int | nx, | |||
| int | sx, | |||
| int | sspec, | |||
| const double | x[], | |||
| double | spec[], | |||
| int | stat[] | |||
| ) |
spcx2s() transforms intermediate world coordinates to spectral coordinates.
| [in,out] | spc | Spectral transformation parameters. |
| [in] | nx | Vector length. |
| [in] | sx | Vector stride. |
| [in] | sspec | Vector stride. |
| [in] | x | Intermediate world coordinates, in SI units. |
| [out] | spec | Spectral coordinates, in SI units. |
| [out] | stat | Status return value status for each vector element:
|
| int spcs2x | ( | struct spcprm * | spc, | |
| int | nspec, | |||
| int | sspec, | |||
| int | sx, | |||
| const double | spec[], | |||
| double | x[], | |||
| int | stat[] | |||
| ) |
spcs2x() transforms spectral world coordinates to intermediate world coordinates.
| [in,out] | spc | Spectral transformation parameters. |
| [in] | nspec | Vector length. |
| [in] | sspec | Vector stride. |
| [in] | sx | Vector stride. |
| [in] | spec | Spectral coordinates, in SI units. |
| [out] | x | Intermediate world coordinates, in SI units. |
| [out] | stat | Status return value status for each vector element:
|
| int spctyp | ( | const char | ctype[], | |
| char | stype[], | |||
| char | scode[], | |||
| char | sname[], | |||
| char | units[], | |||
| char * | ptype, | |||
| char * | xtype, | |||
| int * | restreq | |||
| ) |
spctyp() checks whether a CTYPEia keyvalue is a valid spectral axis type and if so returns information derived from it relating to the associated  -,
-, 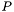 -, and
-, and  -type spectral variables (see explanation above). It recognizes and translates AIPS-convention spectral
-type spectral variables (see explanation above). It recognizes and translates AIPS-convention spectral CTYPEia keyvalues.
The return arguments are guaranteed not be modified if CTYPEia is not a valid spectral type; zero-pointers may be specified for any that are not of interest.
| [in] | ctype | The CTYPEia keyvalue, (eight characters with null termination). |
| [out] | stype | The four-letter name of the  -type spectral variable copied or translated from ctype. If a non-zero pointer is given, the array must accomodate a null- terminated string of length 5. -type spectral variable copied or translated from ctype. If a non-zero pointer is given, the array must accomodate a null- terminated string of length 5. |
| [out] | scode | The three-letter spectral algorithm code copied or translated from ctype. Logarithmic ('LOG') and tabular ('TAB') codes are also recognized. If a non-zero pointer is given, the array must accomodate a null-terminated string of length 4. |
| [out] | sname | Descriptive name of the  -type spectral variable. If a non-zero pointer is given, the array must accomodate a null-terminated string of length 22. -type spectral variable. If a non-zero pointer is given, the array must accomodate a null-terminated string of length 22. |
| [out] | units | SI units of the  -type spectral variable. If a non-zero pointer is given, the array must accomodate a null-terminated string of length 8. -type spectral variable. If a non-zero pointer is given, the array must accomodate a null-terminated string of length 8. |
| [out] | ptype | Character code for the 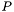 -type spectral variable derived from ctype, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. -type spectral variable derived from ctype, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. |
| [out] | xtype | Character code for the  -type spectral variable derived from ctype, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. Also, 'w' and 'a' are synonymous to 'W' and 'A' for grisms in vacuo and air respectively. Set to 'L' or 'T' for logarithmic (' -type spectral variable derived from ctype, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. Also, 'w' and 'a' are synonymous to 'W' and 'A' for grisms in vacuo and air respectively. Set to 'L' or 'T' for logarithmic ('LOG') and tabular ('TAB') axes. |
| [out] | restreq | Multivalued flag that indicates whether rest frequency or wavelength is required to compute spectral variables for this CTYPEia:
 - and - and  -types) only if -types) only ifrestreq%3 != 0 |
CTYPEia). | int spcspx | ( | const char | ctypeS[], | |
| double | crvalS, | |||
| double | restfrq, | |||
| double | restwav, | |||
| char * | ptype, | |||
| char * | xtype, | |||
| int * | restreq, | |||
| double * | crvalX, | |||
| double * | dXdS | |||
| ) |
spcspx() analyses the CTYPEia and CRVALia FITS spectral axis keyword values and returns information about the associated  -type spectral variable.
-type spectral variable.
| [in] | ctypeS | Spectral axis type, i.e. the CTYPEia keyvalue, (eight characters with null termination). For non-grism axes, the character code for the 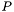 -type spectral variable in the algorithm code (i.e. the eighth character of -type spectral variable in the algorithm code (i.e. the eighth character of CTYPEia) may be set to '?' (it will not be reset). |
| [in] | crvalS | Value of the  -type spectral variable at the reference point, i.e. the -type spectral variable at the reference point, i.e. the CRVALia keyvalue, SI units. |
| [in] | restfrq,restwav | Rest frequency [Hz] and rest wavelength in vacuo [m], only one of which need be given, the other should be set to zero. Neither are required if the translation is between wave-characteristic types, or between velocity-characteristic types. E.g., required for 'FREQ' -> 'ZOPT-F2W', but not required for 'VELO-F2V' -> 'ZOPT-F2W'. |
| [out] | ptype | Character code for the 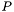 -type spectral variable derived from ctypeS, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. -type spectral variable derived from ctypeS, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. |
| [out] | xtype | Character code for the  -type spectral variable derived from ctypeS, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. Also, 'w' and 'a' are synonymous to 'W' and 'A' for grisms in vacuo and air respectively; crvalX and dXdS (see below) will conform to these. -type spectral variable derived from ctypeS, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. Also, 'w' and 'a' are synonymous to 'W' and 'A' for grisms in vacuo and air respectively; crvalX and dXdS (see below) will conform to these. |
| [out] | restreq | Multivalued flag that indicates whether rest frequency or wavelength is required to compute spectral variables for this CTYPEia, as for spctyp(). |
| [out] | crvalX | Value of the  -type spectral variable at the reference point, SI units. -type spectral variable at the reference point, SI units. |
| [out] | dXdS | The derivative, 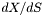 , evaluated at the reference point, SI units. Multiply the , evaluated at the reference point, SI units. Multiply the CDELTia keyvalue by this to get the pixel spacing in the  -type spectral coordinate. -type spectral coordinate. |
| int spcxps | ( | const char | ctypeS[], | |
| double | crvalX, | |||
| double | restfrq, | |||
| double | restwav, | |||
| char * | ptype, | |||
| char * | xtype, | |||
| int * | restreq, | |||
| double * | crvalS, | |||
| double * | dSdX | |||
| ) |
spcxps(), for the spectral axis type specified and the value provided for the  -type spectral variable at the reference point, deduces the value of the FITS spectral axis keyword
-type spectral variable at the reference point, deduces the value of the FITS spectral axis keyword CRVALia and also the derivative 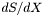 which may be used to compute
which may be used to compute CDELTia. See above for an explanation of the  -,
-, 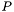 -, and
-, and  -type spectral variables.
-type spectral variables.
| [in] | ctypeS | The required spectral axis type, i.e. the CTYPEia keyvalue, (eight characters with null termination). For non-grism axes, the character code for the 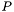 -type spectral variable in the algorithm code (i.e. the eighth character of -type spectral variable in the algorithm code (i.e. the eighth character of CTYPEia) may be set to '?' (it will not be reset). |
| [in] | crvalX | Value of the  -type spectral variable at the reference point (N.B. NOT the -type spectral variable at the reference point (N.B. NOT the CRVALia keyvalue), SI units. |
| [in] | restfrq,restwav | Rest frequency [Hz] and rest wavelength in vacuo [m], only one of which need be given, the other should be set to zero. Neither are required if the translation is between wave-characteristic types, or between velocity-characteristic types. E.g., required for 'FREQ' -> 'ZOPT-F2W', but not required for 'VELO-F2V' -> 'ZOPT-F2W'. |
| [out] | ptype | Character code for the 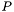 -type spectral variable derived from ctypeS, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. -type spectral variable derived from ctypeS, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. |
| [out] | xtype | Character code for the  -type spectral variable derived from ctypeS, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. Also, 'w' and 'a' are synonymous to 'W' and 'A' for grisms; crvalX and cdeltX must conform to these. -type spectral variable derived from ctypeS, one of 'F', 'W', 'A', or 'V'. Also, 'w' and 'a' are synonymous to 'W' and 'A' for grisms; crvalX and cdeltX must conform to these. |
| [out] | restreq | Multivalued flag that indicates whether rest frequency or wavelength is required to compute spectral variables for this CTYPEia, as for spctyp(). |
| [out] | crvalS | Value of the  -type spectral variable at the reference point (i.e. the appropriate -type spectral variable at the reference point (i.e. the appropriate CRVALia keyvalue), SI units. |
| [out] | dSdX | The derivative, 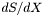 , evaluated at the reference point, SI units. Multiply this by the pixel spacing in the , evaluated at the reference point, SI units. Multiply this by the pixel spacing in the  -type spectral coordinate to get the -type spectral coordinate to get the CDELTia keyvalue. |
| int spctrn | ( | const char | ctypeS1[], | |
| double | crvalS1, | |||
| double | cdeltS1, | |||
| double | restfrq, | |||
| double | restwav, | |||
| char | ctypeS2[], | |||
| double * | crvalS2, | |||
| double * | cdeltS2 | |||
| ) |
spctrn() translates a set of FITS spectral axis keywords into the corresponding set for the specified spectral axis type. For example, a 'FREQ' axis may be translated into 'ZOPT-F2W' and vice versa.
| [in] | ctypeS1 | Spectral axis type, i.e. the CTYPEia keyvalue, (eight characters with null termination). For non-grism axes, the character code for the 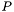 -type spectral variable in the algorithm code (i.e. the eighth character of -type spectral variable in the algorithm code (i.e. the eighth character of CTYPEia) may be set to '?' (it will not be reset). AIPS-convention spectral types are accepted for ctypeS1 but the Doppler frame encoded within them will not be used. |
| [in] | crvalS1 | Value of the  -type spectral variable at the reference point, i.e. the -type spectral variable at the reference point, i.e. the CRVALia keyvalue, SI units. |
| [in] | cdeltS1 | Increment of the  -type spectral variable at the reference point, SI units. -type spectral variable at the reference point, SI units. |
| [in] | restfrq,restwav | Rest frequency [Hz] and rest wavelength in vacuo [m], only one of which need be given, the other should be set to zero. Neither are required if the translation is between wave-characteristic types, or between velocity-characteristic types. E.g., required for 'FREQ' -> 'ZOPT-F2W', but not required for 'VELO-F2V' -> 'ZOPT-F2W'. |
| [in,out] | ctypeS2 | Required spectral axis type (eight characters with null termination). The first four characters are required to be given and are never modified. The remaining four, the algorithm code, are completely determined by, and must be consistent with, ctypeS1 and the first four characters of ctypeS2. A non-zero status value will be returned if they are inconsistent (see below). However, if the final three characters are specified as "???", or if just the eighth character is specified as '?', the correct algorithm code will be substituted (applies for grism axes as well as non-grism). AIPS-convention spectral types are not accepted for ctypeS2. |
| [out] | crvalS2 | Value of the new  -type spectral variable at the reference point, i.e. the new -type spectral variable at the reference point, i.e. the new CRVALia keyvalue, SI units. |
| [out] | cdeltS2 | Increment of the new  -type spectral variable at the reference point, i.e. the new -type spectral variable at the reference point, i.e. the new CDELTia keyvalue, SI units. |
 -type variables.
-type variables.
| const char * spc_errmsg[] |
Error messages to match the status value returned from each function.
 1.5.1
1.5.1